OX-A
Clear anodizing
OX-A is a clear aluminium anodizing treatment in compliance with MIL-A-8625 Type II, and ISO 7599.
OX-A anodizing treatment is composed of an electrolytic aluminium oxidation process. It is performed by dipping the substrate in a sulphuric acid solution at 20°C and by applying direct electric current.
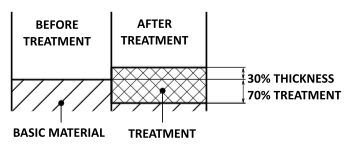
During the process, the surface of the aluminium part is transformed, creating a protective film of aluminium oxide with a typical thickness of 10-20µm.
The OX-A treatment protects treated parts against corrosion and wear. The corrosion resistance of parts anodized with OX-A passes 336 hours in salt spray in compliance with MIL-A-8625.
The treatment is used to protect automatic machinery components, in the medical field, home appliances, and industrial components.




 Technical datasheet
Technical datasheet